1. ASP.NET基础
1.1. ASP.NET静态网页实现简单登录跳转
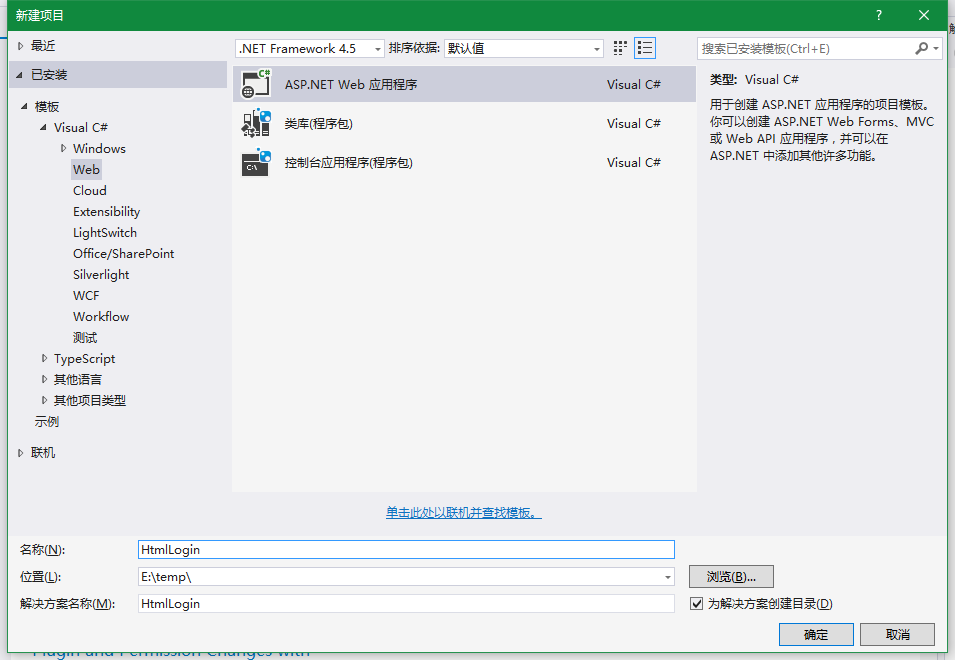
新建Web应用程序,如下图:
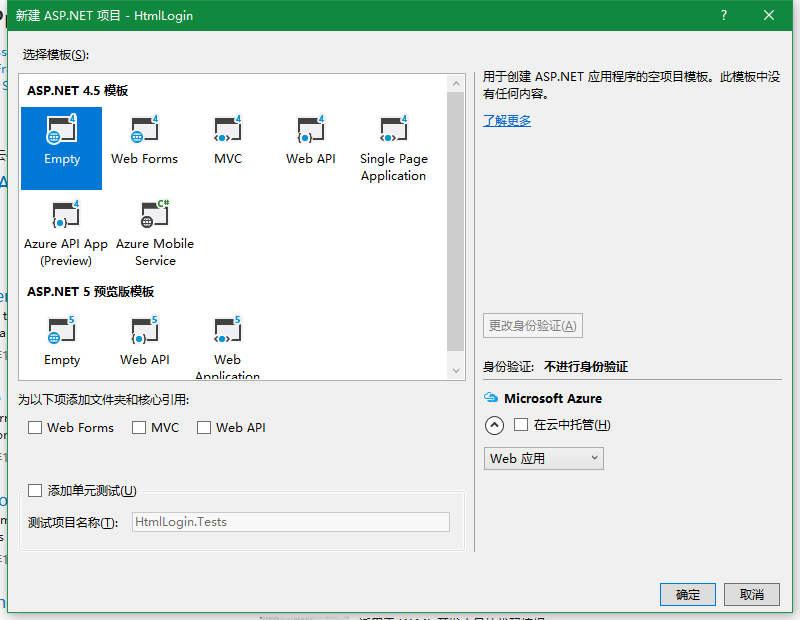
选择Empty空模板,如下图:
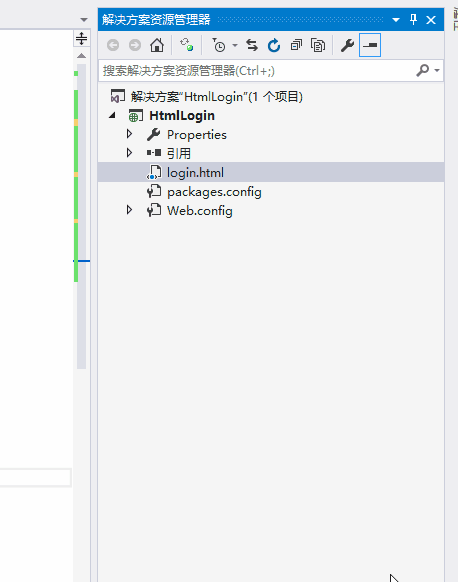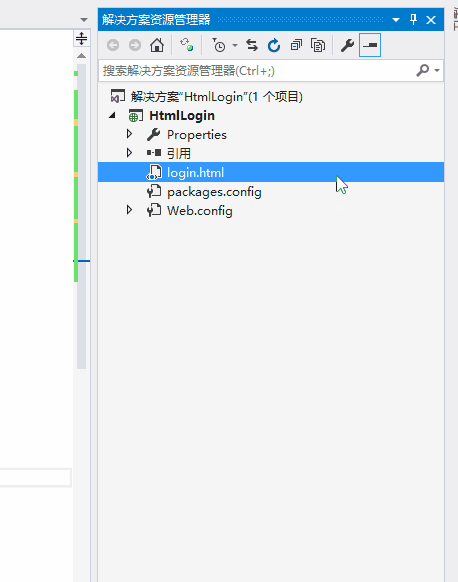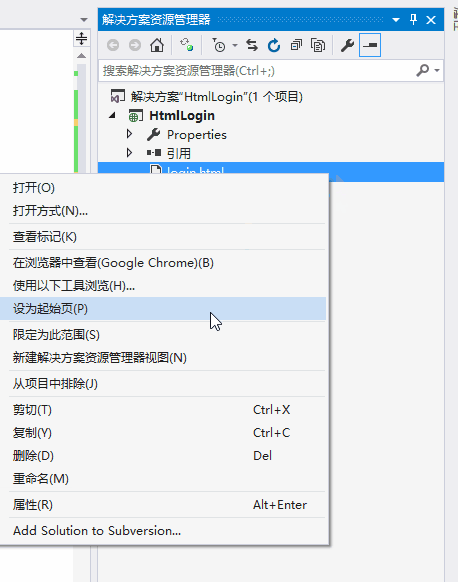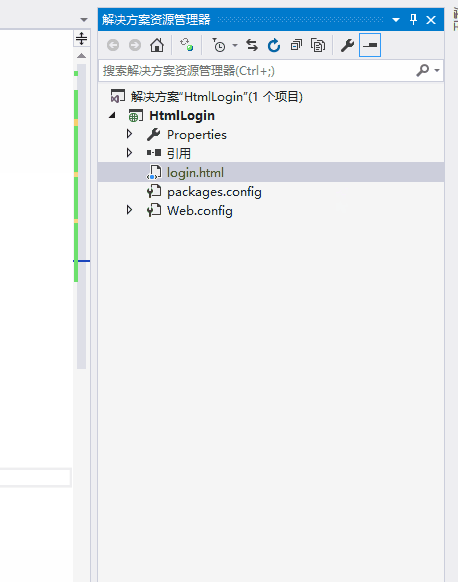
添加Login.html文件并设为起始页,如下图:
Login.html内容如下:
<form>
<fieldset>
<label for="txtName">用户名:</label>
<input type="text" id="txtName" name="name" />
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<label for="txtPwd">密码:</label>
<input type="password" id="txtPwd" name="pwd" />
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<input type="submit" value="登录" />
</fieldset>
</form>
以上,即可以通过开始执行(ctrl+f5)通过浏览器查看该页面。
实现后台的验证功能,通过一般处理程序,接收form表单的提交。新建一般处理程序(HomeHandler.ashx),结构如下:
/// <summary>
/// HomeHandler 的摘要说明
/// </summary>
public class HomeHandler : IHttpHandler
{
/// <summary>
/// 处理http请求
/// </summary>
/// <param name="context"></param>
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
{
context.Response.ContentType = "text/plain";
context.Response.Write("Hello World");
}
/// <summary>
/// 是否重用该处理程序,即多个请求是否访问的一个实例
/// 获取一个值,该值指示其他请求是否可以使用 IHttpHandler 实例。
/// 如果 IHttpHandler 实例可再次使用,则为 true;否则为 false。
/// 默认为false即可
/// </summary>
public bool IsReusable
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
}
修改上述Login.html中form的action为对应的处理程序,如下:
<form id="form1" action="/HomeHandler.ashx" method="post">
修改HomeHandler.ashx一般处理程序的ProcessRequest方法,内容如下:
/// <summary>
/// 处理http请求
/// </summary>
/// <param name="context"></param>
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
{
//修改返回响应的类型,按照html进行解析
context.Response.ContentType = "text/html";
//Request["xxx"]中的xxx对应表单中元素的name属性,而不是id属性!
string name = context.Request["name"];
string pwd = context.Request["pwd"];
if (name == "admin" && pwd == "1")
{
context.Response.Write("<script>alert('登录成功!');</script>");
}
else
{
context.Response.Write("<script>alert('用户名或密码错误!');</script>");
}
}
通过表单提交,即可进行再后台进行验证登录是否成功。以上,就是一个简单的登录demo。
拓展,可以添加另外一个页面Index.html,实现验证成功后跳转到另一个静态页面,在验证成功后添加如下跳转代码:
context.Server.Transfer("Index.html");
对于一个一般处理程序,可能需要处理多个请求,比如登录请求,注册请求等,为了方便方法的调用,我们采用反射的方式进行方法的调用
针对上面的案例,修改如下:
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
{
// 获取方法名称,需要在form表单action属性同步进行修改
string method = context.Request.PathInfo.Substring(1);
//根据前端方法名称反射获取当前Handler类的方法
MethodInfo methodInfo = this.GetType().GetMethod(method);
// 手动进行调用
if(methodInfo != null)
{
methodInfo.Invoke(this, new object[] { context });
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 方法名和form表单action拼接的方法名保持一致
/// 反射进行调用
/// </summary>
/// <param name="context"></param>
public void Login(HttpContext context)
{
context.Response.ContentType = "text/html";
string name = context.Request["name"];
string pwd = context.Request["pwd"];
if (name == "admin" && pwd == "1")
{
context.Server.Transfer("Home.html");
}
else
{
context.Response.Write("<script>alert('用户名或密码错误');</script>");
context.Server.Transfer("Login.html");
}
}
并修改上述Login.html中form的action为对应的处理程序增加/Login方法名,如下:
<form id="form1" action="/HomeHandler.ashx/Login" method="post">
但是上面这种方案会有一个问题,表单提交就会发生跳转,无论验证成功与否。这个问题后面会讲到。。。
1.2. 状态管理
在开发互联网程序时,不可避免的几个问题需要解决:
- 程序数据有些是某个用户独享,而有些是所有用户共享,这块如何设计?
- 用户在浏览器中输入的数据如何传递给服务器,在服务器中又该如何存储管理?
所谓“状态管理”,是指使用ASP.NET中的ViewState、Cookie、Session和Application等对象实现页面数据缓存和传递的技术。
在ASP.NET中,状态管理会被划分为两大类:

可以说状态管理对象依附在内置对象而工作的。下面是这些内置对象的常见属性和方法:
Context
.Cache["key"]
.Session["key"]
.Request
.Cookies["key"] //获取客户端的cookie值
.QueryString["key"] //收集 http get请求传递的数据
.Form["key"] //收集 http post 请求传递的数据
.Server
.Transfer(string url) //终止当前页,执行一个新页
.UrlEncode(string str) //对字符串进行URL编码
.UrlDecode(string str) //对字符串进行URL解码并返回结果
.Response
.Cookies["key"] //设置发送给客户端的Cookie值
.Redirect(string url) //重定向到另一个URL
.Write(string str) //将数据以超文本格式发送到浏览器上
其中:
- Request:HTTP请求对象,用于收集从客户端传递而来的信息。
- Response:HTTP响应对象,用于收集服务器端的信息,并发送到浏览器。
- Context:当前上下文对象,封装了与当前页关联的信息。
1.2.1. 数据缓存
| 方法 | 信息量大小 | 作用域和保存时间 | 应用范围 | 保存位置 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application | 任意大小 | 整个应用程序的生命周期 | 整个应用程序/所有用户 | 服务器端 |
| Cache | 任意大小 | 可以根据需要设定 | 整个应用程序/所有用户 | 服务器端 |
| Session | 小量,简单的数据 | 用户活动时间+一段延迟时间(一般为20分钟) | 单个用户 | 服务器端 |
| Cookie | 小量,简单的数据 | 可以根据需要设定 | 单个用户 | 客户端 |
| 隐藏域 | 小量,简单的数据 | 一个Web页面的生命期 | 单个用户 | 客户端 |
| 查询字符串 | 小量,简单的数据 | 直到下次页面跳转请求 | 单个用户 | 客户端 |
可以在全局应用程序类(Global.asax)中进行数据缓存的模拟。
Session
要想在.ashx中引用 session 必须 using System.Web.SessionState ,继承IReadOnlySessionState/IRequiresSessionState
IReadOnlySessionState,为只读的session 不可以修改
IRequiresSessionState ,可以修改。
单用户数据独享时使用,属于会话级别对象;
允许通过将对象存储在 Web 服务器的内存中在整个用户会话过程中保持任何对象;
每个用户的Session对象是通过SessionID来识别的,该SessionID默认是由客户端的Cookie来存储并传输的。
Session可以保存任何类型的值,包括类的实例:Session["UserName"] = " jack ";
//存放信息
Session["key"]="value";
//读取数据
string UserName = Session["key"].ToString();
// Outside of Web Forms page class, use HttpContext.Current.
HttpContext context = HttpContext.Current;
context.Session["FirstName"] = firstName;
firstName = (string)(context.Session["FirstName"]);
设置session过期时间
<configuration>
<system.web>
<!--设置会话过期时间,timeout单位为分钟-->
<sessionState timeout="1"></sessionState>
<compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.5" />
<httpRuntime targetFramework="4.5" />
</system.web>
</configuration>
Application
多用户数据共享时使用,属于应用程序级别对象;用它保存的数据会在一个应用内多个用户信息共享,并在服务器运行期间持久保存该数据。
服务器一关闭,Application对象就自动消失。允许共享 ASP.NET 应用程序内多个会话和请求之间的全局信息。
在服务器内存中存储数量较少又独立于用户请求的数据:Application["key"] = value ;
Application.Lock();//同步,避免同时写入
Application["CurrentGuests"] =(int)Application["CurrentGuests"]+ 1;//总在线用户数
Application["AllGuests"] =(int)Application["AllGuests"]+ 1;//访问网站的总用户数
Application.UnLock();//同步结束
考虑多用户的情况,我们使用Application进行记录在线用户数,
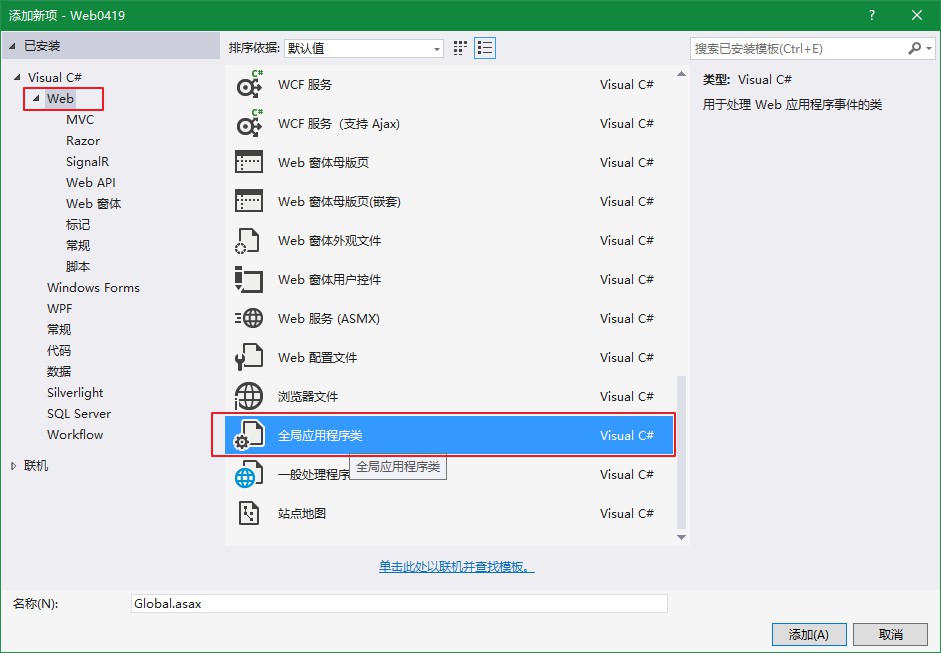
需要处理所有的客户端请求,添加【全局应用程序类】:
public class Global : System.Web.HttpApplication
{
/// <summary>
/// 网站启动的时候会被调用
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
protected void Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e) { }
/// <summary>
/// 某一个session启动的时候会被调用
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
protected void Session_Start(object sender, EventArgs e) { }
/// <summary>
/// 当一个请求过来的时候会被调用,html静态文件是iis直接把文件给到浏览器
/// 不经过asp.net引擎处理,所以不会调用Application_BeginRequest方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
protected void Application_BeginRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { }
/// <summary>
/// 当安全模块已经建立了当前用户的标识后执行。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
protected void Application_AuthenticateRequest(object sender, EventArgs e) { }
/// <summary>
/// 当web应用程序发生错误的时候会被调用
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
protected void Application_Error(object sender, EventArgs e) { }
/// <summary>
/// 当session结束的时候会被调用,如session超时,设置session 20分钟过期,到了这时间就被调用
/// 只有进程内session,也就是InProc(默认模式)过期的时候才会调用Session_End,进程外session不会调用此方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
protected void Session_End(object sender, EventArgs e) { }
/// <summary>
/// 当web应用程序退出的时候会被调用
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
protected void Application_End(object sender, EventArgs e) { }
}
前面说到的记录在线用户数,就需要使用Application_Start事件,Session_Start事件和Session_End事件
在Application_Start程序启动时将计数归零,Session_Start和Session_End会话开始和结束的时候分别做加减。
Cache
Cache对象用于在HTTP请求间保存页面或数据。该对象的使用可以极大地提高整个应用程序的效率。
常用于将频繁访问的大量服务器资源存储在内存中,
当用户发出相同的请求后服务器不再次处理而是将Cache中保存的信息返回给用户,节省了服务器处理请求的时间。
其生存期依赖于该应用程序的生存期。
当重新启动应用程序时,将重新创建其Cache对象的实例。使用Cache对象保存信息的代码如下。
//存放信息
context.Cache["nameID"]="0001";
//存放信息
context.Cache.Insert("nameID","0001");
//读取信息
string NameID = context.Cache["nameID"].ToString();
Cookie
Cookie 提供了一种在 Web 应用程序中存储用户特定信息的方法。
例如,当用户访问您的站点时,您可以使用 Cookie 存储用户首选项或其他信息。
当该用户再次访问您的网站时,应用程序便可以检索以前存储的信息。
/*
cookie的设置方式一
*/
context.Response.Cookies["name"] = name;
context.Response.Cookies["pwd"] = pwd;
context.Response.Cookies["name"].Expires = DateTime.Now.AddHours(1);//设置过期时间为1小时
context.Response.Cookies["pwd"].Expires = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(1);//设置过期时间为1分钟
/*
cookie的设置方式二
*/
HttpCookie hcookie = new HttpCookie("CurAdmin");
hcookie.Value = "zhangsan";
//30s后过期
hcookie.Expires = DateTime.Now.AddSeconds(30);
context.Response.Cookies.Add(hcookie);
/*
cookie的读取
*/
if (context.Request.Cookies["name"] != null)
{
string userName = context.Request.Cookies["name"].Value;
}
/*
不能直接删除用户计算机中的 Cookie。
但是,可以通过将 Cookie 的到期日期设置为过去的日期,让用户的浏览器来删除 Cookie。
当用户下一次向设置该 Cookie 的域或路径内的页发出请求时,浏览器将确定该 Cookie 已到期并将其移除。
*/
if (context.Request.Cookies["CurUser"] != null)
{
HttpCookie myCookie = new HttpCookie("CurUser");
myCookie.Expires = DateTime.Now.AddDays(-1d);
context.Response.Cookies.Add(myCookie);
}
//js读取cookie
document.cookie;
js.cookie
A simple, lightweight JavaScript API for handling browser cookies
github开源项目,封装了cookie操作的API。
github:https://github.com/js-cookie/js-cookie
Basic Usage基本使用:
//Create a cookie, valid across the entire site:
Cookies.set('name', 'value');
//Create a cookie that expires 7 days from now, valid across the entire site:
Cookies.set('name', 'value', { expires: 7 });
//Create an expiring cookie, valid to the path of the current page:
Cookies.set('name', 'value', { expires: 7, path: '' });
//Read cookie:
Cookies.get('name'); // => 'value'
Cookies.get('nothing'); // => undefined
//Read all visible cookies:
Cookies.get(); // => { name: 'value' }
//Delete cookie:
Cookies.remove('name');
//Delete a cookie valid to the path of the current page:
Cookies.set('name', 'value', { path: '' });
Cookies.remove('name'); // fail!
Cookies.remove('name', { path: '' }); // removed!
对象的保存,需要进行JSON格式的转换:
Cookies.set('stu', JSON.stringify({ name:"lucy",age:12 }));
Cookies.get(); // => { stu: "{"name":"lucy","age":12}" }
Cookies.get('stu'); // => '{"name":"lucy","age":12}'
JSON.parse(Cookies.get('stu')); // => {name: "lucy", age: 12}
1.2.2. 数据传递问题
Request
请求对象,用来从客户端取得信息,包括浏览器种类、用户输入表单的数据、Cookies中的数据等信息。
当客户端发出请求执行asp.net程序时,CLR会将客户端的请求信息包含在Request对象中。
可以通过Request.
- QueryString:收集请求url地址中"?"号后面的数据
- Form:收集post方法传递的数据
- Cookies:获取客户端的Cookie值
- ServerVariables:获得环境变量值
Response
响应对象,用于将服务器端的信息发送到浏览器,包括:
- 将服务器端的数据用超文本的格式发送到浏览器上:Response.Write(“js脚本或html脚本”);
- 重定向浏览器到另一个URL:Response.Redirect(“url”, true);
- 设置Cookie的值:Response.Cookies.Add(cookie);
1.3. Ajax
ajax是一种技术方案,但并不是一种新技术。
它依赖的是现有的CSS/HTML/Javascript,而其中最核心的依赖是浏览器提供的XMLHttpRequest对象。
使用 XMLHttpRequest(XHR)对象可以与服务器交互。
可以从URL获取数据,而无需让整个的页面刷新。
这允许网页在不影响用户的操作的情况下更新页面的局部内容。
1.3.1. 构造函数
XMLHttpRequest()该构造函数用于初始化一个 XMLHttpRequest 对象。
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
1.3.2. 方法open()
XMLHttpRequest.open() 方法初始化一个请求。该方法要从JavaScript代码使用;
/*
method:要使用的HTTP方法,比如「GET」、「POST」、「PUT」、「DELETE」、等。对于非HTTP(S) URL被忽略。
url:一个DOMString表示要向其发送请求的URL。
async 可选:一个可选的布尔参数,默认为true,表示要不要异步执行操作。如果值为false,send()方法直到收到答复前不会返回。如果true,已完成事务的通知可供事件监听器使用。
user 可选:可选的用户名用于认证用途;默认为null。
password 可选:可选的密码用于认证用途,默认为null。
*/
xhrReq.open(method, url, [async, user, password]);
1.3.3. 方法send()
XMLHttpRequest.send() 方法用于发送 HTTP 请求。
如果是异步请求(默认为异步请求),则此方法会在请求发送后立即返回;
如果是同步请求,则此方法直到响应到达后才会返回。
XMLHttpRequest.send() 方法接受一个可选的参数,其作为请求主体;
如果请求方法是 GET 或者 HEAD,则应将请求主体设置为 null。
1.3.4. 方法setRequestHeader()
XMLHttpRequest.setRequestHeader() 是设置HTTP请求头部的方法。
此方法必须在 open() 方法和 send() 之间调用。
方法的第一个参数 header 大小写不敏感,即可以写成content-type。
Content-Type的默认值与具体发送的数据类型有关。
需要注意的是,xhr.send(data)中data参数的数据类型会影响请求头部content-type的默认值:
- 如果data是 Document 类型,同时也是HTML Document类型,则content-type默认值为text/html;charset=UTF-8;否则为application/xml;charset=UTF-8;
- 如果data是 DOMString 类型,content-type默认值为text/plain;charset=UTF-8;
- 如果data是 FormData 类型,content-type默认值为multipart/form-data; boundary=[xxx]
- 如果data是其他类型,则不会设置content-type的默认值
通常在post请求时,将参数以键值对方式传递(name1=value1&name2=value2),将【content-type】设置为:
//发送合适的请求头信息
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
1.3.5. 使用XMLHttpRequest对象来发送一个Ajax请求
原生js的ajax请求流程:
1)创建XMLHttpRequest对象
var req = new XMLHttpRequest();
2)发送AJAX请求
GET请求:
req.open('GET', '/Handlers/AjaxHandler.ashx?username=zhangsan&sex=boy');
req.send(null);
------------------------------------------------------------
POST请求:
req.open('POST', '/Handlers/AjaxHandler.ashx');
// 发送合适的请求头信息,必不可少!
req.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
req.send('username=zhangsan&sex=boy');
3)接收AJAX响应
req.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (req.readyState == XMLHttpRequest.DONE && req.status == 200) {
alert('响应消息的正文内容:' + req.responseText);
}
};
其中,readyState可以取如下值:
0 (未初始化,XMLHttpRequest对象已经创建,但尚未初始化,还没有调用open方法)
1 (已经调用send方法,正在发送HTTP请求)
2 (send方法调用结束,已经接收到全部HTTP响应消息)
3 (正在解析响应内容,但状态和响应头还不可用)
4 (完成)
status 返回了XMLHttpRequest 响应中的数字状态码,status码是标准的HTTP status codes
1** 信息,服务器收到请求,需要请求者继续执行操作
2** 成功,操作被成功接收并处理
3** 重定向,需要进一步的操作以完成请求
4** 客户端错误,请求包含语法错误或无法完成请求
5** 服务器错误,服务器在处理请求的过程中发生了错误
get请求:
var xhr =
原生js封装ajax流程:
//调用示例
myAjax({
url: '/Handler/HomeHandler.ashx/Add',
type: 'POST',
data: {
name: name,
pwd: pwd
},
success: function (data) {
if (data == 'true') {
alert('注册成功');
} else {
alert('未注册成功');
}
},
error: function (err) {
alert('请求发生异常');
console.error(err);
}
});
/*
参数说明:
option = {
url:'',//请求的地址
type:'POST',//请求类型 POST或GET
data:{},//传输的数据
success:function(data){},//成功响应后的回调函数
error:function(err){},//失败后的回调函数
}
*/
function myAjax(option) {
//1、创建XMLHttpRequest对象
var req = new XMLHttpRequest();
//默认为GET方式
option.type = option.type || "GET";
//2、发送AJAX请求
if (option.type == "GET") {
req.open('GET', option.url, true);
req.send(null);
} else {
req.open('POST', option.url, true);
req.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
req.send(formatParams(option.data));
}
//3、接收AJAX响应
/*
其中,readyState可以取如下值:
0 (未初始化,XMLHttpRequest对象已经创建,但尚未初始化,还没有调用open方法)
1 (已经调用send方法,正在发送HTTP请求)
2 (send方法调用结束,已经接收到全部HTTP响应消息)
3 (正在解析响应内容,但状态和响应头还不可用)
4 (完成)
*/
req.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (req.readyState == XMLHttpRequest.DONE && req.status == 200) {
option.success(req.response);
} else if (req.readyState == XMLHttpRequest.DONE) {
option.error(req.response);
}
}
}
//格式化参数
function formatParams(data) {
var arr = [];
for (var name in data) {
// encodeURIComponent方法在编码单个URIComponent(指请求参数)应当是最常用的,它可以将参数中的中文、特殊字符进行转义,而不会影响整个URL。
arr.push(encodeURIComponent(name) + "=" + encodeURIComponent(data[name]));
}
arr.push(("v=" + Math.random()).replace(".", ""));
return arr.join("&");
}
escape()、encodeURI()、encodeURIComponent()区别详解
1.4. JSON
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成。它可以构建以下两种结构:
- “名称/值”对的集合
- 值的有序列表(数组)
JSON在大多数的情况下作为AJAX的数据交换格式而不是XML。因为JSON有一些明显的优点:
- 语法更简单,数据传输量更少
- Javascript解码JSON数据容易并且效率高
关于JSON格式:
- key值必须由引号包含;例如推荐使用
{"name":"jack"}格式,不要使用{name:"jack"} - value部分,除数值和布尔值必须也要用引号包含;
在JavaScript中提供了JSON对象,帮助我们将js对象转换为json字符串或者是将json字符串转换为js对象。
//将js对象转换为字符串
JSON.stringify({name:'jack',age:12});// '{"name":"jack","age":12}'
//将js数组转换为字符串
JSON.stringify(['jack','lucy','smith']);// '["jack","lucy","smith"]'
//将复杂对象转换为字符串 -> '{"region":"芜湖市","citys":["镜湖区","弋江区","鸠江区","三山区"]}'
JSON.stringify({region:'芜湖市',citys:['镜湖区','弋江区','鸠江区','三山区']});
//将字符串转换为对象
JSON.parse('{"id":123,"userid":"coder1"}');// {id: 123, userid: "coder1"}
1.4.1. 对象和JSON格式互相转换
Newtonsoft.Json(推荐)
使用第三方 Newtonsoft.Json.net进行序列化和反序列化:
Serialize JSON
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Apple";
product.Expiry = new DateTime(2008, 12, 28);
product.Sizes = new string[] { "Small" };
string json = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(product);
// {
// "Name": "Apple",
// "Expiry": "2008-12-28T00:00:00",
// "Sizes": [
// "Small"
// ]
// }
Deserialize JSON
string json = @"{
'Name': 'Bad Boys',
'ReleaseDate': '1995-4-7T00:00:00',
'Genres': [
'Action',
'Comedy'
]
}";
Movie m = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<Movie>(json);
string name = m.Name;
// Bad Boys
Newtonsoft默认序列化会带来一个问题,时间格式中默认会有一个【T】,可以通过修改时间格式解决:
JsonConvert.SerializeObject(list, new IsoDateTimeConverter() { DateTimeFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" });
System.Runtime.Serialization
使用.NET提供的功能,需要添加System.Runtime.Serialization.dll引用
/// <summary>
/// C#对象 转换成 JSON字符串
/// </summary>
/// <param name="item">C#对象</param>
/// <returns>JSON字符串</returns>
public static string ToJson(object item)
{
DataContractJsonSerializer serializer = new DataContractJsonSerializer(item.GetType());
using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream())
{
serializer.WriteObject(ms, item);
string str = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(ms.ToArray());
// 将其中的 "" 转化成“-”
str = str.Replace("\"\"", "\"-\"");
// 替换Json的Date字符串
string p = @"\\/Date\((\d+)\+\d+\)\\/";
MatchEvaluator matchEvaluator = new MatchEvaluator(delegate (Match m)
{
return new DateTime(1970, 1, 1).AddMilliseconds(long.Parse(m.Groups[1].Value))
.ToLocalTime().ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
});
Regex reg = new Regex(p);
str = reg.Replace(str, matchEvaluator);
return str;
}
}
如需将对象进行序列化操作,需要针对类添加特性标记。
无法序列化类型“xxxxx”。
请考虑将其标以 DataContractAttribute 特性,并将其所有要序列化的成员标以 DataMemberAttribute 特性。
如果类型为集合,则请考虑将其标以 CollectionDataContractAttribute 特性。
/// <summary>
/// 后端处理返回前端数据的封装
/// 包含操作成功标记,以及相应的文本信息
/// </summary>
[DataContract]
public class ResultState
{
public ResultState(bool status, string msg)
{
Status = status;
Message = msg;
}
[DataMember]
public bool Status { get; set; }
[DataMember]
public string Message { get; set; }
}
1.5. 跨域
同源策略是一种约定,它是浏览器最核心也最基本的安全功能,如果缺少了同源策略,浏览器很容易受到XSS、CSRF等攻击。
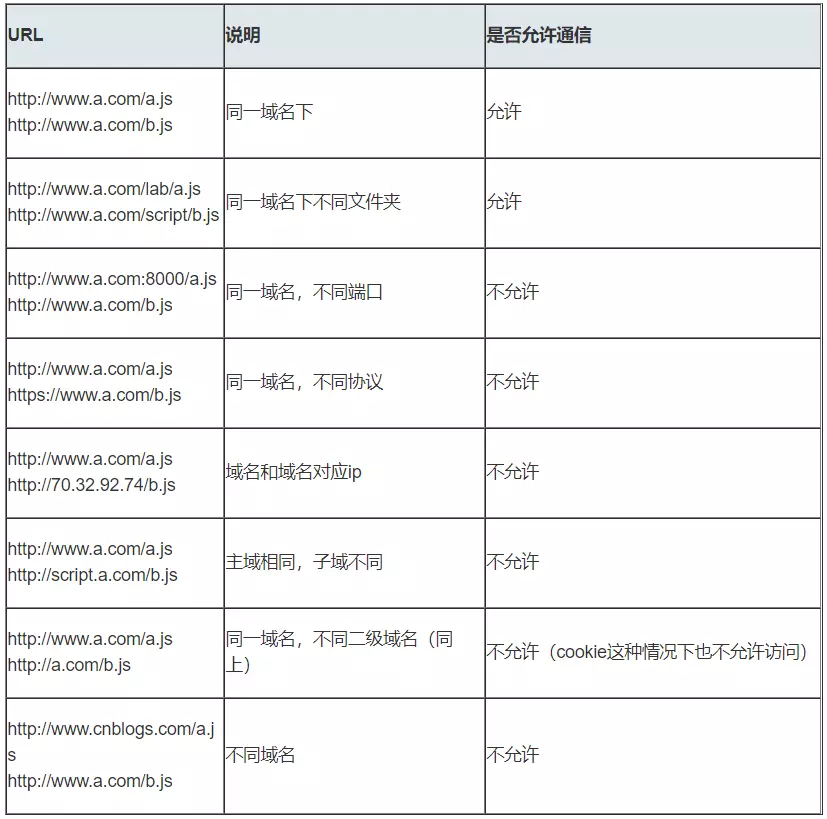
所谓同源是指"协议+域名+端口"三者相同,即便两个不同的域名指向同一个ip地址,也非同源。

同源策略限制内容有:
- Cookie、LocalStorage、IndexedDB 等存储性内容
- DOM 节点
- AJAX 请求发送后,结果被浏览器拦截了
但是有三个标签是允许跨域加载资源:
<img src=XXX><link href=XXX><script src=XXX>
当协议、子域名、主域名、端口号中任意一个不相同时,都算作不同域。不同域之间相互请求资源,就算作"跨域"。
常见跨域场景如下图所示:
跨域并不是请求发不出去,请求能发出去,服务端能收到请求并正常返回结果,只是结果被浏览器拦截了。
1.5.1. 一般处理程序-CORS
有【Student】类如下:
class Student
{
public Student(int score) { Score = score; }
public int Score { get; set; }
public string Judge
{
get
{
if (Score < 60) { return "未通过"; }
else { return "已通过"; }
}
}
}
一般处理程序【HomeHandler】,根据请求参数分数返回学生对象
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
{
int score = int.Parse(context.Request["score"]);
Student s = new Student(score);
context.Response.Write(Newtonsoft.Json.JsonConvert.SerializeObject(s));
}
发布网站,通过url进行访问:
http://localhost:9001/HomeHandler.ashx?score=90
// output: {"Score":90,"Judge":"已通过"}
创建新的项目,模拟跨域访问
$.ajax({
url: 'http://localhost:9001/HomeHandler.ashx',
dataType: 'json',
data: { score: 90 },
method: 'post',
}).done(function (resp) {
console.log(resp);
}).fail(function (err) {
console.error(err);
}).always(function (resp) {
console.info('finish');
});
/*
抛出异常信息如下:
Access to XMLHttpRequest at 'http://localhost:9001/HomeHandler.ashx'
from origin 'http://localhost:59399' has been blocked by CORS policy:
No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource.
*/
可以通过修改一般处理程序允许跨域访问,修改【ProcessRequest】方法:
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
{
// 允许跨域访问
context.Response.AddHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
int score = int.Parse(context.Request["score"]);
Student s = new Student(score);
context.Response.Write(Newtonsoft.Json.JsonConvert.SerializeObject(s));
}
新增【Access-Control-Allow-Origin】设置,原请求即可以正常访问。
以上是通过修改后台方法实现,较为简单。
1.5.2. JSONP
JSONP是JSON with Padding的略称。
它是一个非官方的协议,它允许在服务器端集成Script tags返回至客户端,
通过javascript callback的形式实现跨域访问(这仅仅是JSONP简单的实现形式)。
在上述案例中,修改一般处理程序【HomeHandler】如下:
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
{
// 参数中指定的回调函数名
string callback = context.Request["callback"];
int score = int.Parse(context.Request["score"]);
Student s = new Student(score);
string jsonStr = Newtonsoft.Json.JsonConvert.SerializeObject(s);
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
// 返回形式:callback(data),即在客户端进行调用
context.Response.Write($"{callback}({jsonStr})");
}
前端以jquery封装ajax为例进行jsonp调用:
$.ajax({
url: 'http://localhost:9001/HomeHandler.ashx',
dataType: 'jsonp',
jsonpCallback: 'getResult',
data: { score: 90 },
method: 'post',
}).done(function (resp) {
console.log(resp);
}).fail(function (err) {
console.error(err);
}).always(function (resp) {
console.info('finish');
});
function getResult(data) {
debugger;
}
创建一个回调函数,然后在远程服务上调用这个函数并且将JSON 数据形式作为参数传递,完成回调。
1.5.3. 和风天气调用
可以跨域访问:
$.ajax({
url: 'https://free-api.heweather.net/s6/weather/now',
dataType: 'json',
method: 'post',
data: {
key: '5a731c7828654c36b2cdca90c38058b1',
location: 'wuhu'
}
}).done(function (resp) {
console.log(resp);
}).fail(function (err) {
console.error(err);
});
1.5.4. 心知天气调用跨域案例
无法直接跨域访问:
$.ajax({
url: 'https://api.seniverse.com/v3/weather/now.json',
dataType: 'json',
method: 'post',
data: {
key: 'SdkANqWkZKziScAnm',
location: 'wuhu'
}
}).done(function (resp) {
console.log(resp);
}).fail(function (err) {
console.error(err);
});
/*
抛出异常信息:
Access to XMLHttpRequest at 'https://api.seniverse.com/v3/weather/now.json'
from origin 'http://localhost:59399' has been blocked by CORS policy:
No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource.
*/
在一般处理程序中可以实现如下封装:
public class WeatherHandler : IHttpHandler
{
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context)
{
// 查询天气的城市
string location = context.Request["location"];
// 基本url
string baseUrl = "https://api.seniverse.com/v3/weather/now.json";
// 个人账户的key值
string key = "SdkANqWkZKziScAnm";
// 拼接天气查询url
string url = $"{baseUrl}?key={key}&location={location}";
// 模拟请求调用
HttpWebRequest req = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(url);
req.Method = "GET";
HttpWebResponse res = (HttpWebResponse)req.GetResponse();
string jsonStr = string.Empty;
using (Stream stream = res.GetResponseStream())
{
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(stream, Encoding.UTF8);
jsonStr = sr.ReadToEnd();
}
context.Response.Write(jsonStr);
}
public bool IsReusable
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
}
前端直接进行调用接口:
$.getJSON('/WeatherHandler.ashx?location=wuhu', function (data) {
console.log(data);
});
1.6. 疑难杂症
1.6.1. CompositionFailedException
参考 Javascript and css intellisense not working
由 Microsoft 在 2015/5/14 於 14:17 公佈 Giacomo,
Would you please try the following:
- Exit Visual Studio
- Delete the following folder
%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\VisualStudio\14.0\ComponentModelCache
That folder is hidden by default, so you may need to change Windows Explorer settings in order to see it (you can follow steps similar to http://windows.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/show-hidden-files#show-hidden-files=windows-7).
- Re-start Visual Studio and see if the issue is resolved.
I would appreciate if you would let us know if that resolved your issue.
Thanks, Alex Gavrilov 由 Microsoft 在 2015/4/29 於 8:04 公佈 Thank you for your feedback, we are currently reviewing the issue you have submitted. If you require immediate assistance with this issue, please contact product support at http://support.microsoft.com/ph/1117.
参考引用: